RGB and HSV are two ways to describe the same visible color. RGB says how much red, green, and blue light to mix on a display. HSV rewrites that color as a hue angle, a saturation amount, and a value that feels like brightness.
Designers like HSV because rotating hue shifts color families cleanly, while raising or lowering value acts like a simple brightness control. Engineers keep RGB close because it is what screens draw and what most image files store. Knowing how to move between them without surprises will save rework and head scratching.
Screens and sensors work with three primaries. Each pixel emits red, green, and blue light in fixed ratios defined by the device’s color space, commonly sRGB on consumer hardware. The numbers in an 8 bit RGB file are not linear light though. They are gamma encoded so that small changes near dark tones are visible to the eye. That encoding is useful for storage and display. It does mean that math done directly on those values can be misleading if you forget the gamma curve hiding underneath.
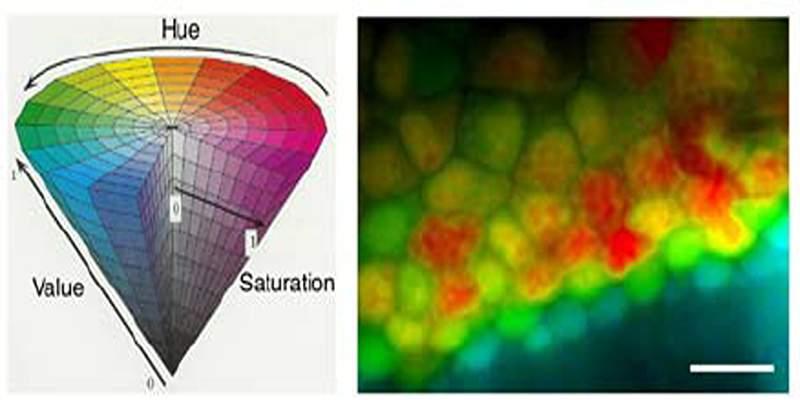
HSV takes a color and places it on a wheel. Hue is an angle from 0 to 360 that wraps, so red near 0 sits next to red near 360. Saturation measures how far the color is from the center. At the center, saturation is zero and the color becomes a gray with no tint. Value measures the height of the color from black up to full brightness. Many people find edits in HSV more intuitive because they match how we talk about color families and intensity.
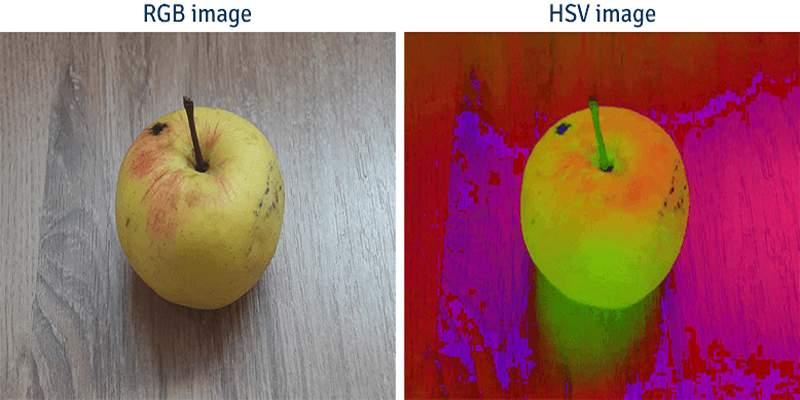

A clean mental model helps. First think about brightness. The value channel in HSV mirrors the maximum of the three RGB primaries once the numbers sit in a common scale. That is why V tracks the strongest channel. Saturation then measures how far the smallest channel sits from that maximum. If the strongest and weakest channels are equal, the color is on the gray line, so saturation goes to zero and hue becomes undefined. Most software pegs hue at zero in that case and hides it from sliders.
Hue needs one more step. It is defined by which primary is strongest and where the middle channel lands between strongest and weakest. That placement maps to an angle on the color wheel. Because the wheel wraps, negative angles get shifted forward by adding 360 so that hue always sits within a standard range. Precision matters near the wrap. A tiny rounding error should not flip red at 359 into red at 1, or your gradients will kink.
The return trip partitions the hue wheel into six slices that align with primary and secondary colors. Within the active slice, the algorithm mixes the value and saturation to find the three RGB channels. One receives the full value, one gets a reduced amount, and one lands at a level in between based on where the hue falls inside that slice. After that mix, values are clamped to the expected range and, if needed for storage, re-encoded into the file’s gamma curve.
This path is reversible when precision is kept. If you round aggressively or clip early, small hue shifts may appear where you expected none. Keeping math in floating point until the very end preserves smooth ramps and avoids banding.
Neutral colors deserve special attention. When red, green, and blue are equal, the color is gray. HSV sets saturation to zero, and hue is not meaningful. Any system that exposes a hue control should freeze it during such moments instead of jumping to a default.
Very dark colors can surprise you. In near black regions, small numeric changes can swing hue wildly even though the color looks almost the same. That is because the ratio of channels dominates when values are tiny. If your workflow edits shadows heavily, consider applying a small floor before converting, or edit in a linear light space first, then convert to HSV for cosmetic tweaks.
Gamma matters more than most expect. sRGB stores values with a curve that follows human vision. HSV formulas assume the numbers represent intensities on a straight line. If you feed gamma encoded RGB into the math, saturation may not behave the way your eye expects. For accurate work, decode to linear light, convert to HSV, make your edits, convert back to linear RGB, then re-encode to sRGB for storage. Many libraries hide this step, which can be fine for casual edits but risky for precise work.
Different tools use near twins with similar names. HSL replaces value with lightness that averages the top and bottom of the RGB channels. Adobe tools often write HSB, which is a legacy name for HSV. These models map sliders differently. HSL tends to keep midtones flatter when you sweep hue, while HSV tracks brightness by the strongest channel. Pick the model that matches your tool and stick with it inside a given project. Switching midstream can create subtle mismatches across assets.
RGB is the right place for compositing, blending, and anything that depends on physical mixing of light. It is also the final stop before encoding images for display. HSV shines for creative tweaks. Rotating hue changes color families while preserving perceived intensity. Nudging saturation controls intensity of color without a complex mask. Adjusting value acts like a simple brightness control that leaves hue alone. Use HSV for decisions that should feel human, then return to RGB for storage and delivery.
Color ramps expose small mistakes fast. If you create a gradient in HSV by interpolating hue angles across the wrap, the jump from 359 to 1 may go the long way around the wheel and pass through colors you did not intend. The fix is simple. Interpolate on the circle by choosing the shorter arc direction, or temporarily unwrap the angles so the numbers drift smoothly through the boundary. After interpolation, wrap the result back into the 0 to 360 range. Apply the same care to saturation and value so steps feel even, not choppy.
Eight bit channels can band when you edit aggressively in HSV because many operations compress or expand narrow ranges. Working at higher bit depth keeps more shades between steps. If you must deliver at eight bits, do heavy edits in a higher depth workspace, then dither on export. Dithering spreads tiny errors and hides banding from the eye, which keeps backgrounds and soft shadows looking natural.
RGB and HSV describe the same colors from different angles, one built for devices, the other shaped for human editing. Move from RGB to HSV by tracking the strongest channel, measuring spread for saturation, and mapping that balance to a hue angle that wraps cleanly. Come back by picking the right slice on the wheel and mixing channels from value and saturation.
Guard against pitfalls by decoding sRGB to linear light before heavy math, freezing hue on grays, treating near black with care, and interpolating hue along the short path around the circle. With those habits in place, your edits feel natural, your gradients stay smooth, and your files land on screens without unwelcome surprises.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
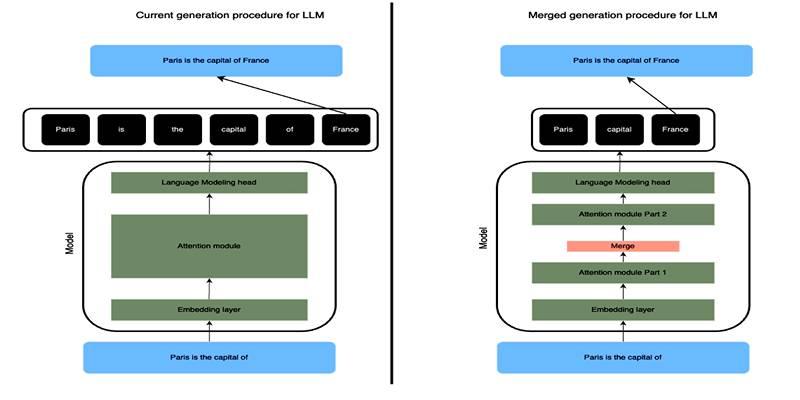
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
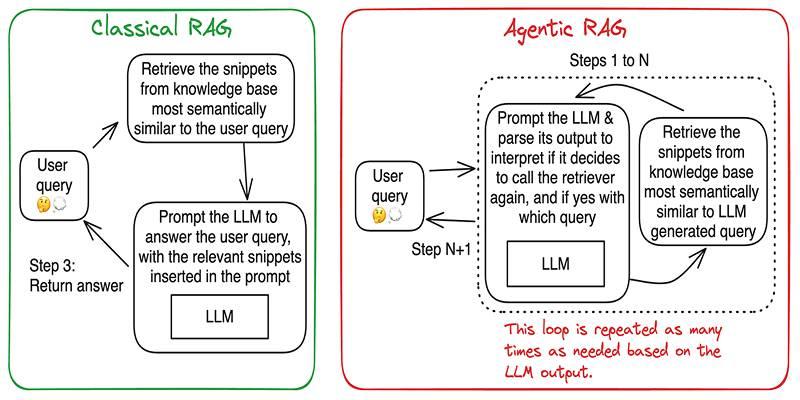
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development