In today’s world, organizations generate massive data every day, from social media activity to transaction logs and sensor readings. Efficient processing of this data is critical for gaining insights and staying competitive. MapReduce, introduced by Google, distributes large datasets across clusters of computers.
It divides tasks into smaller pieces and runs them in parallel, ensuring speed and reliability for big data workloads. In this article, we explore how MapReduce transforms big data processing and why it is essential for modern enterprises.
MapReduce is a programming model designed to process and generate large-scale datasets efficiently. It simplifies complex tasks into two primary functions: Map and Reduce.
Using this model, organizations can perform large-scale computations without worrying about low-level details such as parallelization, fault tolerance, or load balancing.
MapReduce offers several features that make it indispensable for large-scale data processing:
These features collectively make MapReduce ideal for organizations processing vast amounts of structured or unstructured data.
MapReduce relies on several critical components that ensure its efficiency, scalability, and reliability:
These components work together to deliver efficient, scalable, and fault-tolerant processing of massive datasets.
MapReduce is particularly effective in big data environments due to its distributed and parallel processing approach.
For Example: Analyzing web server logs to track user behavior. Each log line is mapped to a key-value pair and then reduced to count page views per user. The process can scale to billions of log entries without manual intervention.
The MapReduce workflow involves several key steps:
This workflow ensures tasks are executed efficiently, even on datasets spanning terabytes or petabytes.
MapReduce is a cornerstone of modern big data architectures because it enables organizations to process massive datasets efficiently and reliably. Compounds can scale horizontally across hundreds or thousands of nodes by dividing tasks into parallelizable maps and reducing operations.
This ensures high throughput and fault tolerance; as failed tasks are automatically retried without disrupting the job. Consequently, MapReduce empowers enterprises to handle growing data volumes, extract meaningful insights, and maintain performance across distributed systems.
MapReduce is widely used across industries to solve complex data problems:
These applications demonstrate MapReduce’s ability to scale across sectors while delivering actionable insights.
MapReduce provides several advantages that make it essential for enterprise data systems:

These advantages explain why MapReduce remains a core technology for big data processing in enterprises.
MapReduce has revolutionized how organizations handle massive datasets. It processes data in parallel across clusters, ensures fault tolerance, and handles diverse data types. These capabilities make it essential for enterprise data systems. From e-commerce to healthcare, MapReduce empowers businesses to extract insights and optimize operations.
By adopting MapReduce, enterprises can confidently manage growing data volumes. Start adopting MapReduce today to explore faster and more efficient data processing for your enterprise.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
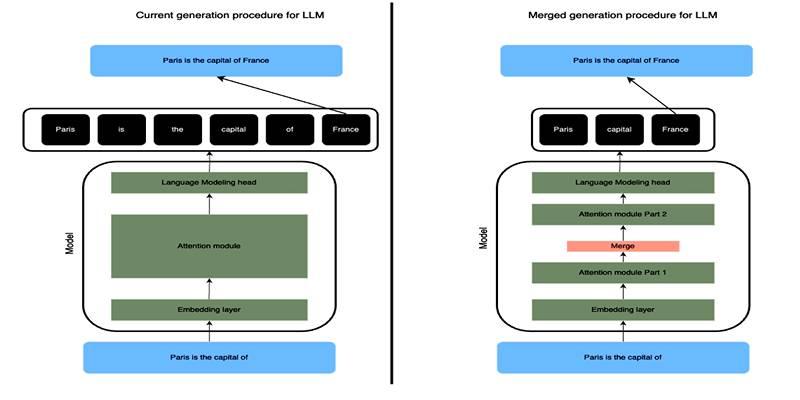
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
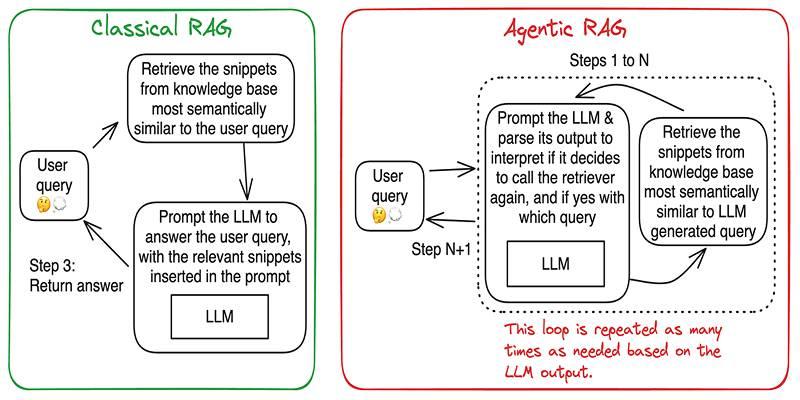
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
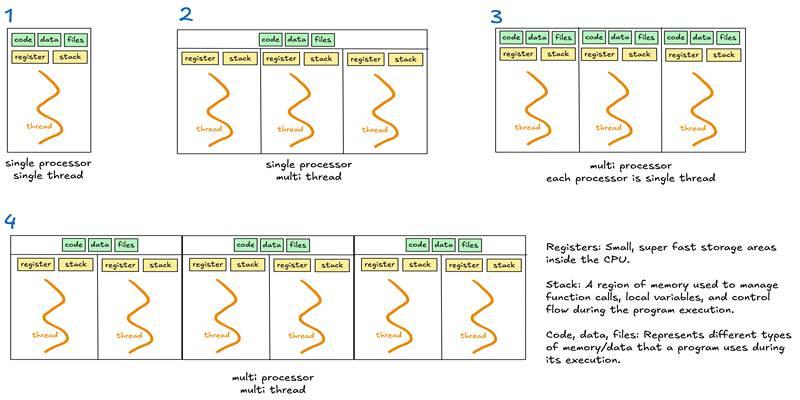
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development