A good data dictionary turns a messy workbook into a shared map that anyone on the team can read. It explains what each sheet holds, what every column means, how values are shaped, and who owns the truth when questions come up. Excel is still where many business datasets begin, so it helps to generate this map right where people work instead of in a separate tool that only a few folks open.
OpenPyxl can read the structure of a workbook without launching Excel, while AI agents can draft plain language descriptions that save hours. Put the two together with a light review loop, and you get a clear, living dictionary that earns trust.
OpenPyxl can load workbooks, read sheet names, step through header rows, and peek at values to guess types. Treat the first nonempty row as the header unless your team uses a standard position. Infer types by sampling values, not by trusting the first cell, since many files start with an empty or placeholder entry. Keep the scan gentle.
Record the column order, the count of non-null cells, and a quick profile of distinct values or basic patterns. These signals help the agent write grounded summaries and help reviewers spot oddities.
Once the scanner collects structure and samples, pass compact prompts to an agent that can write short descriptions. The agent should read the sheet title, the column name, a few representative values, and any obvious patterns such as dates or codes.
Ask for one or two clear sentences that a non-technical teammate can understand. Keep temperature low so phrasing stays steady across columns. Where samples are mixed or unclear, the agent should say that the column needs a human description rather than inventing a story. Honesty here prevents later confusion.
Types in Excel can be slippery, so write both an inferred type and a normalized type that your team accepts, such as integer, decimal, date, date time, text, or categorical. Add a simple rule field for patterns that matter, like an ISO date format or a specific code mask. Store a short example pulled from real data. These three fields together make validation easier later and give readers a feel for the data without opening the sheet.
Many workbooks carry names, emails, phone numbers, or identifiers. The agent can propose sensitivity tags based on column names and sampled values, but a human should confirm them. Keep tags simple and consistent, for example public, internal, confidential, or restricted. Add a note on handling rules if a column contains sensitive details, such as mask in exports or share only with a named group. Clear tags stop accidental leaks and speed audits.
A dictionary becomes far more useful when it points to relationships. If two sheets share a key, note it in both places. If a column is a foreign key, record the parent sheet and field. Add an owner field that names the person or team that sets the rules for that sheet. Ownership turns vague disputes into quick questions and short answers. It also helps during changes, since the right people can approve updates to definitions.
Put the dictionary inside the same workbook so users can find it. A dedicated sheet called Data Dictionary keeps things obvious. Place fixed columns in a consistent order so eyes know where to look. Freeze the header row, add filters, and keep descriptions short enough to read without expanding cells across the screen. If the workbook has many sheets, add a summary section at the top that counts columns by sensitivity and flags fields that need review. Little touches like these invite regular use.
Automation makes the first pass quick, but quality still matters. Compare distinct value counts across refreshes to catch sudden shifts. Flag columns where the agent was uncertain so reviewers can fill the gaps. Track a simple completeness score that measures how many required dictionary fields are filled for each column. When the scanner sees a column rename or a dropped field, record the change in a small log on the same sheet. Clear signals make maintenance calm.

Agents write fast, yet humans carry context. Schedule a light review where a domain expert reads the new or changed rows and edits phrasing. Keep edits human in tone and avoid jargon that only one team understands. When definitions change, add a short reason, such as source system update or policy shift. These notes help future readers and stop repeat debates. For big changes, ask both the data owner and a consumer team to review so you balance intent with usage.
Treat the dictionary as a living artifact. When the workbook is stored in a shared drive or a versioned repository, include the scan date in a small cell near the top and the creator in another cell. Save a lightweight export to CSV for teams that prefer reading in other tools. If several workbooks feed a central store, collect their dictionaries into a master catalog, but keep the sheet level view inside each file. People appreciate finding the map where they work.
Run the OpenPyxl scan to collect structure and samples. Draft descriptions with the agent using compact prompts that include names, values, and patterns. Write results to the Data Dictionary sheet in a fixed layout. Review uncertain rows with the data owner, edit phrasing, and confirm sensitivity tags. Save, share, and log the scan date. Schedule a refresh on a cadence that matches how often the workbook changes. Small, steady updates keep quality high.
A data dictionary for Excel does not have to be heavy or hard to maintain. OpenPyxl can read the workbook quietly, gather structure, and extract examples, while AI agents can propose short descriptions that sound clear to everyday readers. Add careful types, simple rules, sensitivity tags, and ownership notes, then place everything in a tidy sheet that ships with the data.
Keep light checks, short reviews, and a basic change log so the dictionary grows with the file instead of falling out of date. When teams can open a workbook and find clear meaning next to the numbers, questions shrink, trust rises, and work moves with far less friction.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
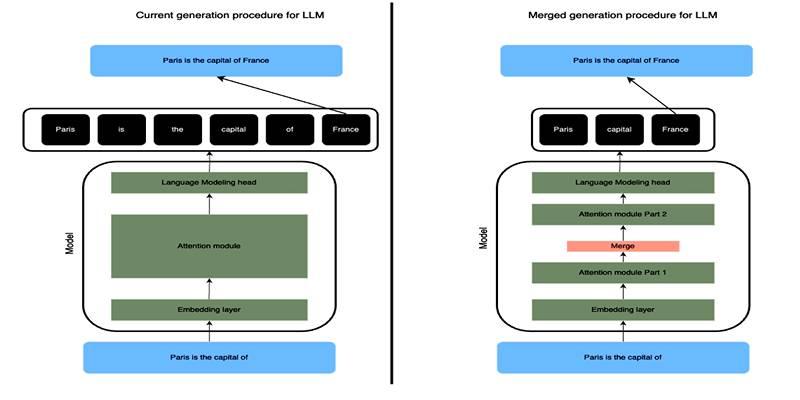
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
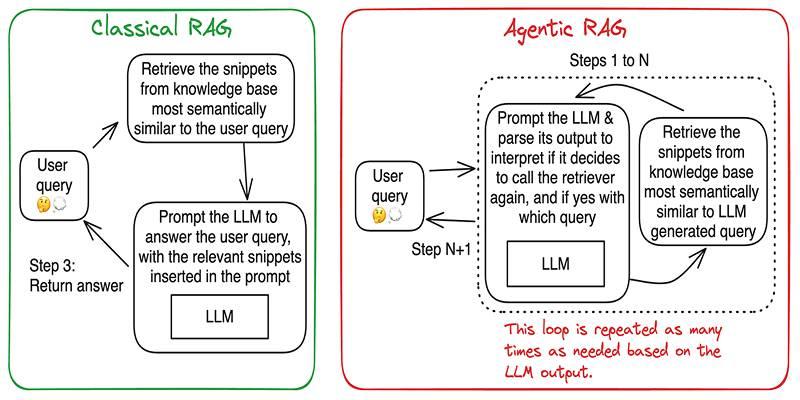
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development