In the modern competitive data science market, it is important to be familiar with the basics of Software engineering. Inheritance software engineering is one of these core principles that enable data scientists to develop scalable, maintainable, and efficient codebases. Based on object-oriented programming (OOP), Inheritance has enabled programmers to design classes that have similar functionality with specialization in subclasses. This article defines the importance of the data scientists' inheritance concepts in the context of helping to maintain reusable code, how this concept encourages people to adopt this concept, and how individuals who embrace the concept of mastery of this concept distinguish themselves as professional data scientists.

Computer programming Inheritance is the concept that enables a specific type of class to be shown to have the properties and methods of another type of class, referred to as the parent or superclass. This allows the subclass the chance to utilize the code of the parent with the introduction or alteration of the features that are exclusive to the subclass. Shear, Inheritance also does not cause the reuse of the code to be reproduced; in effect, this assists in encouraging modular and extensible design.
To data scientists, Inheritance implies that you can describe general data processing or modeling behaviour once and then specialise or tailor it easily to various situations. Such a philosophy is in contrast to restructuring similar functions repeatedly, which augments error risk and maintenance costs.
Repetitive tasks can be common in data science projects--data loading, cleaning, feature extraction, or model evaluation. The tasks in adopting the inheritance software engineering may be structured into base classes where the shared logic is encoded. These foundations are then extended by subclasses to address certain data sources, formats, or algorithms. This methodology produces reusable code and ensures a large amount of redundancy is minimized.
This codebase is also more maintainable since all changes as far as the base classes are concerned are automatically propagated to the subclasses. Where a bug is fixed or an optimization introduced in the parent class, every descendant class will gain automatically.
When there are more than two individuals in a team, the compliance with such explicit principles of programming as Inheritance enhances the cooperation significantly. Structured code based on hierarchies of Inheritance is simpler to comprehend and to extend, even for the non-creators themselves. It develops a common style of structuring logic, closing the divide between data scientists and software engineers.
A lot of data scientists begin projects with exploratory scripts or notebooks, which solve short-term issues but are not sustainable. Early application of concepts of Inheritance makes the code modular, testable, and scalable. This is essential in the translation of models and processes between prototypes and production settings, where sound software engineering practices are obligatory.

Awareness of these forms allows data scientists to create their code in a logical way that is not difficult to understand.
Take an example of a project where we have a number of data sources, and each must be loaded, cleaned, and stored. In this underwriting, you start defining a base, in which you will detail the entire pipeline actions instead of defining distinct functions for each data form. These particular details of individual data sources are then introduced in subclasses.
Although it is not excessive, this trend shows how the concept of Inheritance can be used to foster clarity and reuse because it defines the workflow once and permits expansion.
Don't have deep inheritance hierarchies: Have shallow inheritance trees to minimize complexity.
One of the four pillars of object-oriented programming- the rest being encapsulation, abstraction, and polymorphism- is Inheritance. OOP promotes the design of software in terms of interacting objects with responsibilities. To data scientists, applying OOP concepts such as Inheritance would lead to clean code that represents real-life problems, is more debuggable, and can be installed with other current tools.
Knowledge of inheritance software engineering opens the potential of OOP, and data scientists can create and maintain complex workflows.
Finally, to succeed as a data scientist, it is important to know fundamental software engineering, in particular, Inheritance. It allows the formation of reusable code, makes teamwork easier, and makes the way between research prototypes and production-ready solutions easier. The principle of integrating Inheritance into the practice of data science enhances the quality of software, the level of productivity, and makes professionals distinctive in a competitive sphere. Adopting Inheritance will save time, as well as future proof codebases, in a fast moving data world.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
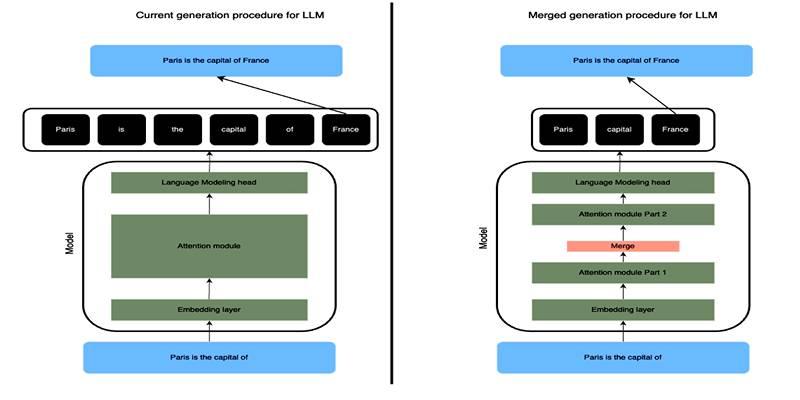
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
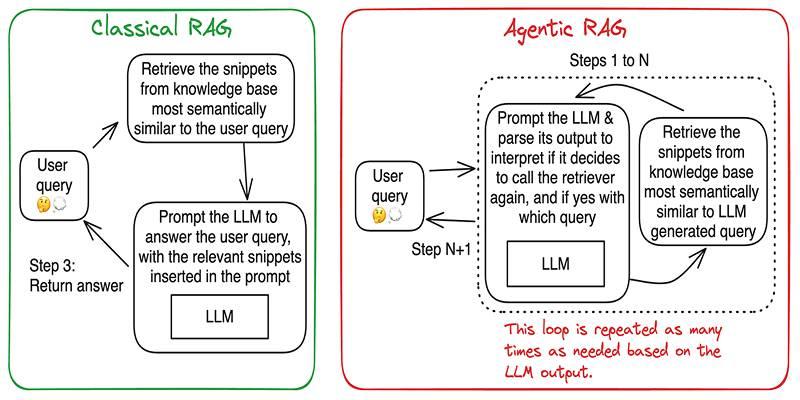
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
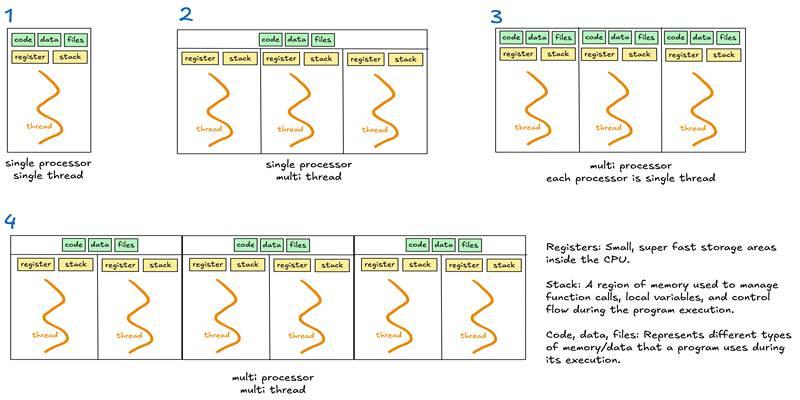
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development