As companies face pressure from investors, authorities, and customers to reduce emissions, there is an increasing urgency to implement sustainable practices. However, manual reporting overwhelms many small sustainability teams. To address this, AI agents for sustainability are emerging. These intelligent technologies swiftly analyse vast volumes of data, providing teams with quicker insights and relieving them of tedious duties. Professionals might put more emphasis on long-term planning and innovation than on manual labour. AI agents are more than just helpers; they are changing how businesses prepare for a greener future by monitoring energy consumption and streamlining supply chains.

While they are both classified as artificial intelligence, generative AI and AI agents differ in their autonomy and goal.
Generative AI focuses on using training data to produce new material, such as text, photos, or designs. Although it does not typically take direct action, it is a creative tool that investigates alternatives.
Conversely, AI agents are designed to act. They can take in their surroundings, make choices, and carry out actions to accomplish objectives, can automatically compile sustainability data, create compliance reports, or recommend emission-reduction tactics.
The two technologies supplement one another in many contemporary business solutions. Although generative AI can generate summaries or innovative ideas, AI agents make sure those ideas result in practical action.
Companies pursuing sustainability often encounter three common obstacles: fragmented data, complex reporting requirements, and limited internal resources. Traditional methods of preparing sustainability reports can take months, requiring manual data collection from multiple systems and databases.
AI agents for sustainability simplify this process. They connect different data sources, organize information into consistent formats, and provide instant access to critical insights. This allows businesses to not only meet compliance requirements but also identify opportunities for efficiency.
Another major advantage lies in regulatory reporting. Across regions, frameworks such as the CSRD in Europe or SASB and GRI elsewhere are demanding detailed disclosures. AI agents can automate the preparation and formatting of these reports, ensuring accuracy while saving teams a considerable amount of time.
By removing technical barriers, AI agents empower non-technical users to interact with sustainability data. A manager could simply ask, “What were our emissions last quarter?” and receive a ready-to-use answer in seconds. This accessibility makes green transformation faster and more achievable.
The adoption of AI agents brings several advantages to organizations pursuing sustainable practices. First, they enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks. What once required a team of analysts can now be handled by an AI agent around the clock.
Second, they deliver precision. Because they process large volumes of structured and unstructured data, their outputs are accurate and consistent. This reliability reduces the risk of errors in sustainability reporting.
Third, they offer scalability. As businesses grow, so does the complexity of their sustainability data. AI agents adapt easily, analyzing increasing volumes without requiring additional human resources.
Perhaps most importantly, AI agents provide actionable insights. Instead of overwhelming teams with raw numbers, they highlight trends, predict outcomes, and recommend effective strategies. This bridges the gap between analytics and execution, making sustainability initiatives more impactful.
The practical applications of AI agents are expanding rapidly, with many companies already seeing tangible benefits. Some of the most promising use cases of AI agents in sustainability include automated reporting, supplier engagement, emissions tracking, and energy optimization.
For example, in supply chain management, AI agents can suggest ways to reduce transportation emissions by optimizing delivery routes. In energy management, they can monitor consumption in real time and recommend efficiency upgrades.
They are also proving useful in stakeholder communication. Instead of manually preparing presentations for investors or regulators, AI agents can generate real-time sustainability updates that are both accurate and easy to understand.
Another growing area is disaster relief and climate response. AI agents can streamline donation matching or coordinate the delivery of resources after natural disasters. These examples show that the technology is not only valuable for compliance but also for building resilience and trust.

Implementing AI agents requires thoughtful preparation. The first step is to assess organizational needs. Companies should define the goals they want to achieve, whether improving reporting accuracy, reducing energy costs, or accelerating supply chain transformation.
Once goals are clear, the next step is to evaluate potential solutions. Businesses must seek platforms that integrate seamlessly with existing systems, respect data privacy, and adhere to ethical standards. Clean and reliable data is crucial, so investing in good data management practices is essential.
Training and support also play a vital role. While many AI agents are designed to be user-friendly, teams still benefit from guidance in customizing them for specific tasks. With the right planning, companies can scale adoption without disrupting operations.
Looking ahead, the role of AI agents in sustainability is expected to continue growing. As regulatory demands increase and environmental concerns intensify, businesses will increasingly rely on automated, intelligent solutions.
Future trends indicate deeper integration with business applications, enabling AI agents to deliver even more insightful information. We can also expect more advanced analytics capabilities, which will provide predictive insights to help organizations prepare for future challenges.
Moreover, as technology improves, AI agents themselves will become more sustainable. Optimized models and energy-efficient designs will reduce their own environmental impact, ensuring they contribute positively to the overall sustainability mission.
The path forward is clear: organizations that embrace AI agents today will be better positioned to meet tomorrow’s environmental and business demands.
More than just a fad, AI agents for sustainability are quickly becoming essential for businesses seeking to strike a balance between growth and accountability. By comprehending the distinctions between generative AI and AI agents, appreciating their unique advantages, and exploring a range of AI agent use cases, businesses can turn sustainability from a burden into a catalyst for innovation. To stay competitive and responsible, start exploring how AI agents can drive your organization’s sustainable transformation today.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
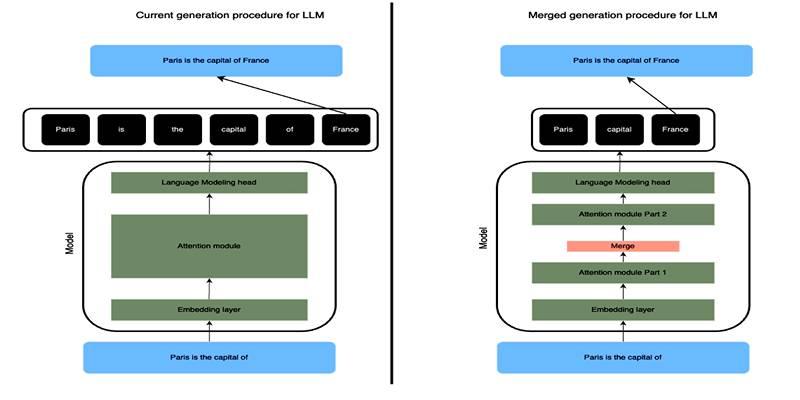
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
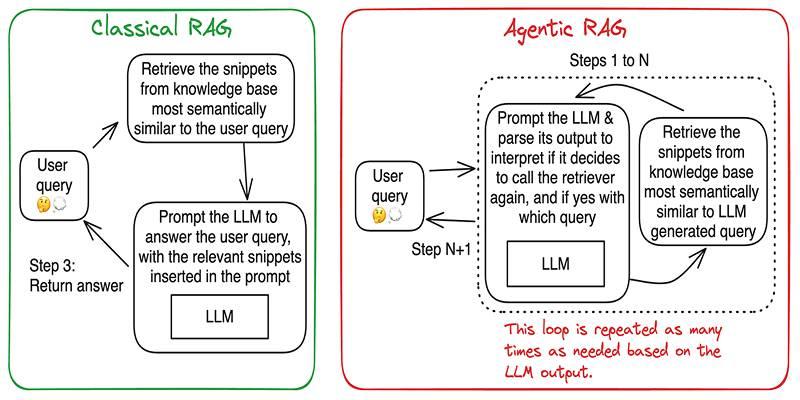
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
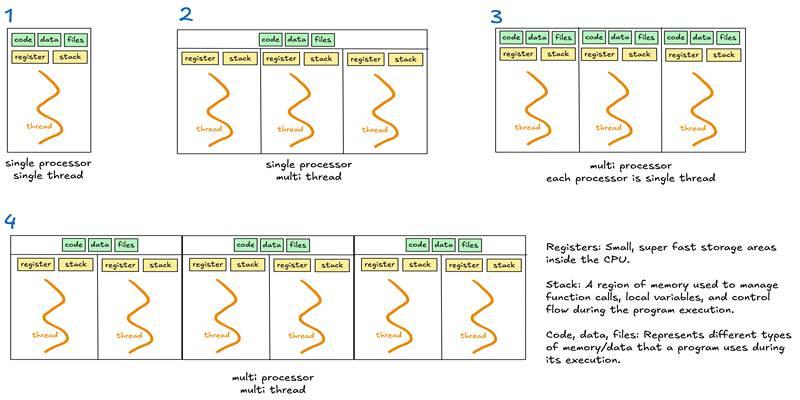
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development