Weak governance in the AI industry has resulted in numerous product launch failures among other things such as biased outputs and privacy concerns. The launch of Grok 4, however, was an outstanding success, acclaimed by users and regulators. Its secret? An effective AI governance policy is put in place well in advance. This policy guide discusses the governance processes that Grok 4 became an example of AI excellence.

The development team at Grok 4 has also organized their governance structure when first planning the application as it would be very expensive and much less effective to insert governance mechanisms in the later stages of the work. This proactive mindset revolved around three key pillars: ethical development of AI, regulatory conformity and stakeholder engagement.
The team began by creating detailed ethical guidelines that went beyond standard industry practices. These guidelines addressed potential bias in training data, fairness in algorithmic decision-making, and transparency in AI outputs. Rather than treating ethics as a checkbox exercise, the development team integrated these principles into daily workflows and decision-making processes.
Each major development milestone included mandatory ethics reviews, conducted by a dedicated team of ethicists, technologists, and domain experts. This ongoing assessment ensured that ethical considerations remained central throughout the development lifecycle, preventing the accumulation of ethical debt that has plagued other AI systems.
Instead of viewing regulatory compliance as a burden, the Grok 4 team treated it as a design constraint that would ultimately strengthen their product. They conducted extensive analysis of existing and proposed AI regulations across multiple jurisdictions, incorporating compliance requirements directly into system architecture.
This approach proved particularly valuable when new AI regulations were introduced during the development process. Because compliance was built into the system's foundation, adapting to new requirements required minimal changes rather than costly redesigns.
The governance framework included a comprehensive risk assessment process that identified potential issues before they could impact users or stakeholders. This proactive risk management approach covered technical risks, ethical concerns, and business implications.
The team implemented rigorous testing protocols that went beyond standard quality assurance measures. They conducted adversarial testing to identify potential vulnerabilities, stress testing to ensure system reliability under high loads, and bias testing to detect unfair outcomes across different user groups.
Red team exercises simulated real-world attack scenarios, helping identify security vulnerabilities and potential misuse cases. These exercises revealed several critical issues that were addressed before launch, preventing what could have been significant post-launch security incidents.
Understanding that AI systems impact diverse stakeholder groups, the team conducted extensive stakeholder mapping and risk analysis. They identified potential negative impacts on different user segments, communities, and industry partners, then developed specific mitigation strategies for each identified risk.
This stakeholder-centric approach informed both technical decisions and communication strategies, ensuring that potential concerns were addressed proactively rather than reactively.
One of the most significant factors in Grok 4's successful launch was the team's commitment to transparent communication with all stakeholders, including users, regulators, researchers, and the general public.
The team published comprehensive documentation about Grok 4's capabilities, limitations, and potential risks well before the launch date. This documentation included technical specifications, use case guidelines, and clear explanations of the system's decision-making processes.
They also created accessible explanations of complex AI concepts, helping non-technical stakeholders understand how the system works and what safeguards are in place. This educational approach built trust and reduced anxiety about the new AI system.
Rather than waiting for regulatory scrutiny, the Grok 4 team actively engaged with relevant regulatory bodies throughout the development process. They shared development updates, sought feedback on compliance measures, and incorporated regulatory suggestions into system design.
This collaborative approach with regulators created a partnership rather than an adversarial relationship, facilitating smoother approval processes and reducing regulatory risks.
The governance framework emphasized inclusive decision-making that incorporated perspectives from diverse stakeholder groups. This approach helped identify potential issues that might have been overlooked by a more homogeneous development team.
The team established an advisory board that included ethicists, social scientists, industry experts, civil society representatives, and affected community members. This diverse group provided ongoing guidance throughout the development process, ensuring that multiple perspectives informed key decisions.
Regular advisory board meetings addressed emerging challenges and provided feedback on proposed solutions. The board's input proved particularly valuable in refining the system's fairness mechanisms and identifying potential unintended consequences.
Recognizing that AI systems impact entire communities, the team implemented extensive community engagement programs. These programs included public forums, focus groups, and pilot testing with representative user groups.
Community feedback directly influenced system design decisions, particularly in areas related to user interface design, accessibility features, and cultural sensitivity. This engagement helped ensure that Grok 4 would serve diverse user needs effectively.

The success of Grok 4's launch offers valuable lessons for other organizations developing AI systems. These insights extend beyond technical considerations to encompass the full spectrum of AI governance challenges.
Perhaps the most important lesson is the value of implementing governance measures from the beginning of the development process. Organizations that attempt to add governance frameworks after development face significantly higher costs and reduced effectiveness.
Early governance implementation allows teams to build safeguards into system architecture rather than adding them as afterthoughts. This approach results in more robust, reliable, and trustworthy AI systems.
Building strong relationships with stakeholders, including regulators, requires ongoing investment and genuine commitment to collaboration. Organizations that view stakeholder engagement as a one-time activity miss opportunities to build trust and gather valuable feedback.
Transparent communication about AI capabilities, limitations, and risks helps build public trust and reduces the likelihood of negative reactions to AI deployments. Organizations should invest in creating clear, accessible documentation and educational materials.
The Grok 4 launch highlights that proactive AI governance is about more than risk mitigation—it's about fostering trust, enabling responsible innovation, and delivering value. By adopting strong governance frameworks, organizations can thrive in a regulated AI environment. Grok 4's success shows how responsible development enhances performance, strengthens stakeholder relationships, and boosts reputation. It offers a blueprint for organizations aiming to launch AI systems with accountability and long-term success.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
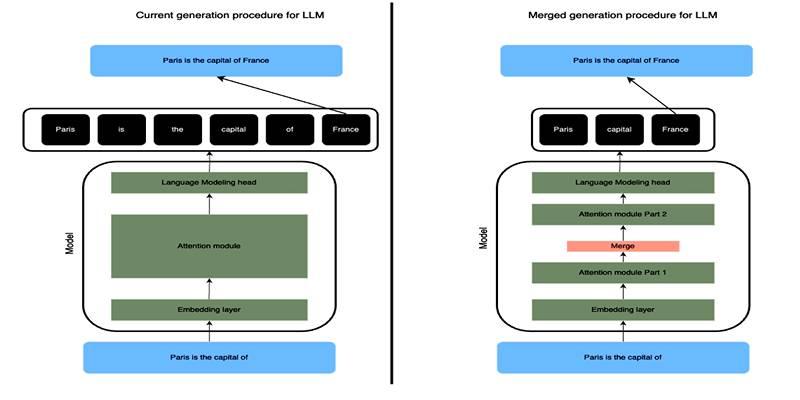
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
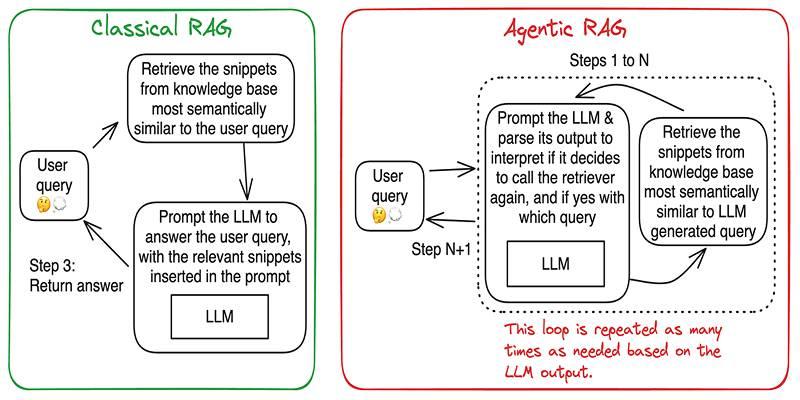
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
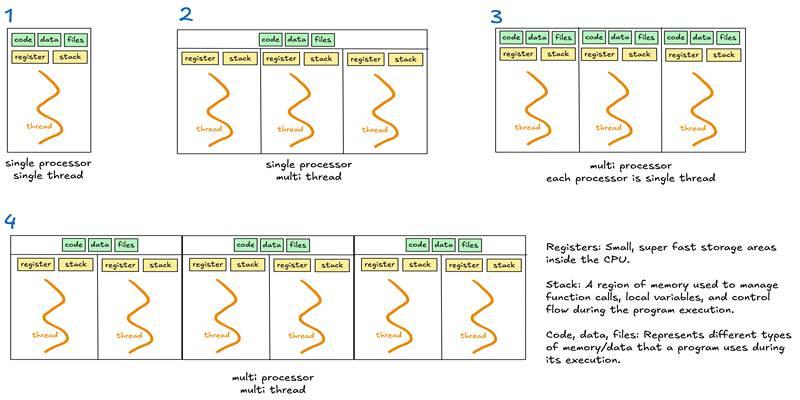
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development