The introduction of the Vision Transformer architecture was a breakthrough in computer vision, as it manages to implement the transformer methodology in image processing. Nonetheless, this innovation had one major constraint, namely, an enormous training data demand. The original Vision Transformer needed hundreds of millions of labeled examples to reach a competitive level of performance, placing impractically considerable barriers to many research teams and organizations that do not have access to extensive computational capabilities.
It was this data dependency problem that motivated researchers to come up with a more accessible alternative. Within only a few months of the initial release of ViT, a collaborative of researchers headed by Hugo Touvron presented Data-efficient image Transformers, a paradigm that cut data requirements by a few orders of magnitude with such impressive accuracy. This new architecture used only a million images, compared to the 300 million pictures required by previous models, a reduction of three hundred-fold in the amount of data needed. The breakthrough was a democratization of transformer-based computer vision, which allowed researchers and developers using limited resources to use it.
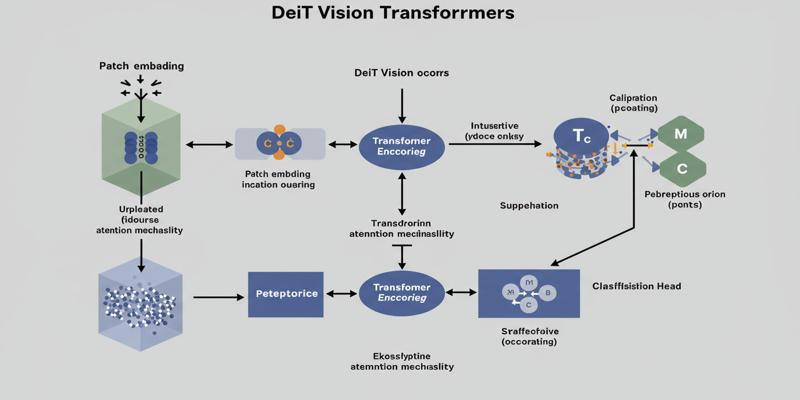
The main novelty of it is the advanced knowledge distillation method, with a small student model acquiring knowledge through the instruction of an experienced teacher model. This framework does not follow the traditional approaches; it uses a convolutional neural network as the teacher to show the transformer-based student throughout the training. This mixed methodology builds on the strengths of both architectures: CNNs incorporate powerful inductive biases to visual processing, and transformers have better global context modelling abilities.
The distillation mechanism allows two types of learning on both ground truth labels and the prediction of the teacher model, which forms an efficient knowledge transfer system. This methodology is much more efficient with samples, in that the model can gain more information per training example, and less data is required in general.
The architecture presents a new concept of distillation token to make it stand apart in comparison to traditional knowledge distillation methods. Although in a conventional vision transformer, the classification was done using a single class token, this new design uses two tokens, the first of which is used in distillation. This token works in parallel with the class token across the transformer layers and allows learning both with labeled data and teacher predictions.
The specialized distillation token is a special input to the teacher model soft labels, and the token is introduced into the course of action to establish a knowledge transfer mechanism, which is more effective than merely adding tokens in classes. Such architectural segregation enables a more apparent distinction between learning objectives and has proven to be more effective in distillation than more traditional approaches.
Several optimization techniques make the framework efficient:
The framework has various variants that can be used to fit multiple resource limitations and performance needs:
Although the fundamental transformer architecture is preserved, several changes allow improvements in computational efficiency:
In-depth assessments show strong performance attributes in several measures. Compared to both convolutional neural networks and other vision transformers, the framework achieves an excellent balance between accuracy and efficiency.
The largest variant attains top-1 accuracy on par with state-of-the-art convolutional networks with much less training data on typical benchmark data sets. The minor variant offers an excellent efficiency-accuracy trade-off, which is appropriate to apply in practice when the computational resources are limited. The most minor variant can provide decent performance with low computation needs.
The architectural breakthroughs have significant computational benefits in various dimensions:
The efficiency improvements open numerous practical applications previously inaccessible to transformer-based vision models:
The flexibility in the architecture enables adaptation to particular applications, such as medical imaging and autonomous systems, at computational performance.
The achievement of data-efficient vision transformers has triggered many research directions and practical applications. The current trends concern the further enhancement of efficiency while preserving the performance characteristics. Scholars are finding methods to improve the knowledge distillation process, create more productive architectural elements, and, finally, streamline the training process to an even smoother one.
The framework has also brought the motivation to consider hybrid methods that could combine the many strengths of convolutional networks with transformers, which may in the future be replaced by even more efficient architectures. These advancements place the limits of what can be done with less computational resources, and advanced computer vision features continue to be made available to researchers and developers all over the world.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
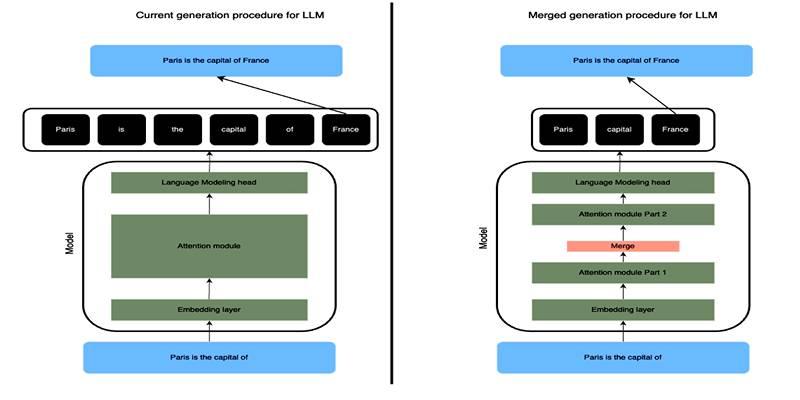
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
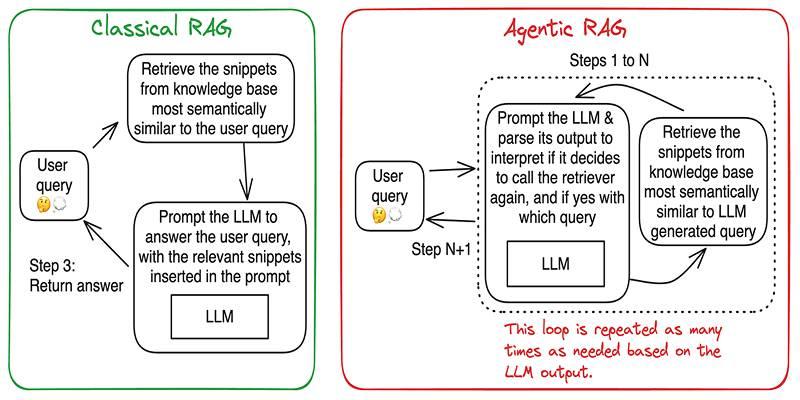
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
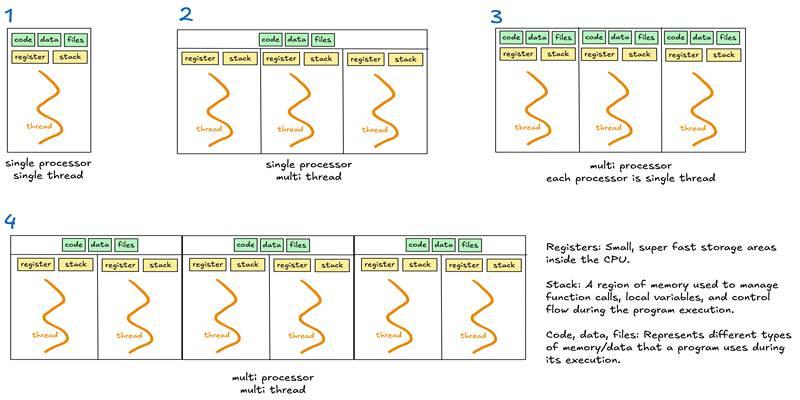
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development