Large language models can feel slow when prompts get long. Each extra token adds work across the attention stack, and that work piles up fast. Token merging tackles the slowdown by fusing nearby, similar tokens into a single stand-in that carries the same idea.
The trick is to combine vectors without washing out their meaning. SLERP, short for spherical linear interpolation, gives a neat path. It blends two unit vectors along the surface of a sphere, keeping direction sharp and magnitude stable. That is the whole idea in one breath: merge redundant tokens, keep their semantic direction, and shorten the sequence the model must read.
A token becomes a vector once it passes through the embedding layer. After normalization, the vector’s direction hints at meaning, while its length acts like strength. If you average two vectors in a straight line, you drift toward the origin and weaken the signal.
SLERP moves along the arc between the vectors on the unit sphere. The angle comes from the dot product, and a mixing weight selects a point on that arc. You end up with a unit vector that points between the inputs without shrinking. This keeps meaning intact and avoids a dull midpoint that the network might treat as low energy.
Good mergers start with smart selection. Look for neighbors in the sequence that have high cosine similarity, since that signals the same idea said twice or minor phrasing changes. Repeated boilerplate often lights up as tight clusters.
You can set a similarity floor so random pairs do not fuse. Keep rare tokens, numbers, negations, and code symbols off limits. Those pieces carry outsized meaning and deserve their own space. A sliding window over the prompt, paired with a cap on the share of tokens merged per window, keeps things steady and predictable.
After you blend two vectors, you still need a position. A simple plan keeps the first token’s position and drops the second. That choice plays nicely with rotary positional embeddings, since you can reuse the original index without recalculating anything fancy.
The model sees a shorter sequence with a token that “feels” like both originals. If your stack supports it, you may encode a soft midpoint, yet most teams find the first-position rule fast, clean, and easy to debug.
Speed is not only about the prefill pass. During generation, key and value caches grow with each token. Long chats and tool calls can swell those caches until memory gets tight. Many entries end up as near duplicates when the prompt repeats patterns.
You can search the cache for highly similar keys or values and merge them with SLERP. This trims memory use and reduces time spent moving tensors. Apply strict thresholds and avoid sensitive heads or layers if you see drift in tests. Even light cache merging can make a laptop or small GPU breathe easier.

The blend weight should reflect importance. If attention scores, token saliency, or simple heuristics hint that one token matters more, lean the weight toward it. When both tokens play equal roles, pick the midpoint.
Another safe rule is to weight by inverse frequency, so common fillers bend toward the rarer neighbor. Keep the math in higher precision for near-parallel vectors, since tiny angles can turn into noisy divisions. When the angle is extremely small, a normalized average is close enough and cheaper to compute.
Any compression brings risk, so guard the edges. Merges can blur small but key words like not or off if you fuse them with a stronger neighbor. Numbers, dates, units, currency symbols, and code markers deserve a no-merge tag.
Names and rare entities also benefit from protection. Keep a strict ceiling on how many tokens you merge per window and across the whole prompt. If a section reads like legal text or medical advice, consider turning merging off for that span. A light touch brings most of the gain with little change to meaning.
Measure before and after with the same prompts. Track prefill latency, tokens per second, peak memory, and cache size. Then check answer quality with a small audit set. Compare n-gram overlap, semantic similarity scores, and human spot checks on tricky cases.
Pay special attention to long prompts with repeated framing text. Those are sweet spots for merging because they contain clusters of near copies. Record both mean and tail latency, since merges often trim the slowest runs the most.

If you ship this feature in a product, explain it in plain terms. People should know when prompts might be compacted during processing. Provide a simple switch to turn it off when fidelity matters more than speed, such as legal reviews or strict audits. For research or hobby use, note the setting in the release notes so others can compare results fairly and reproduce your setup without guessing.
Make the feature accessible and fair from day one. Tell users when compacting is active, ask for consent where needed, and give a plain audit view that shows when merges happened and why. Document known risks, like possible loss of rare details, and state the steps you take to limit them in simple language. Keep reviewers in the loop with change logs and reproducible configs so they can trace behavior across versions.
SLERP-based token merging trims sequence length and eases attention work while keeping meaning pointed in the right direction. The method blends similar token vectors on the unit sphere, places the result back into the sequence, and applies careful rules so key details stay intact.
By guarding sensitive tokens, choosing weights that reflect importance, and limiting how much you merge, you gain faster responses and lower memory use without turning answers mushy. Add clean metrics, roll it out with restraint, and you get a tidy speedup that fits today’s transformer stacks and plays nicely with real prompts that tend to repeat themselves.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
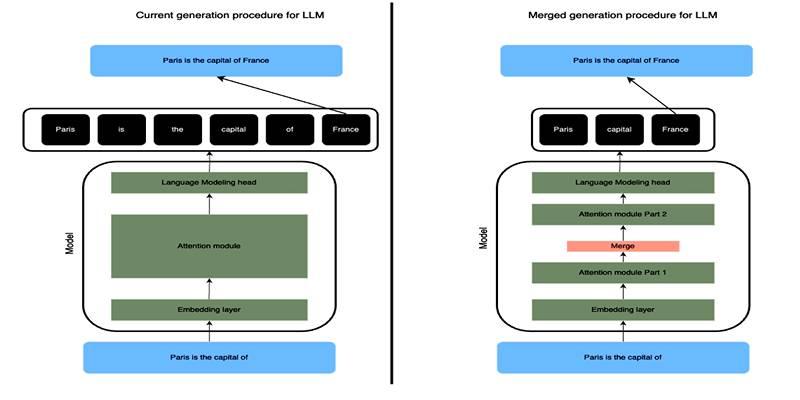
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
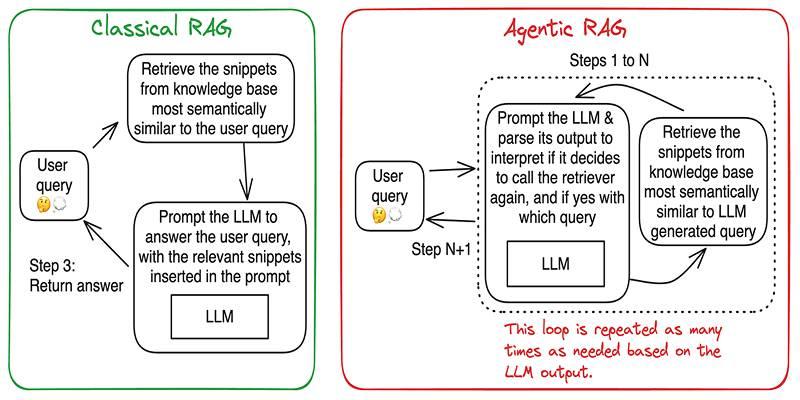
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
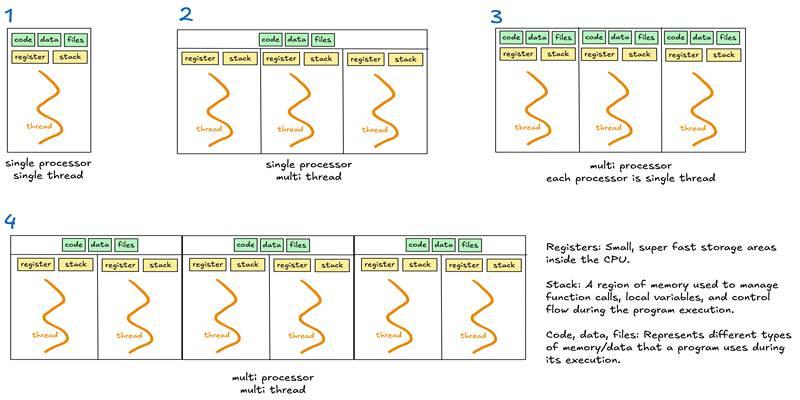
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development