Retrieval augmented generation, or RAG, mixes a language model with a search step so answers are grounded in real sources. Multi-agentic RAG goes a step further by assigning clear roles to several collaborating agents. One agent plans, another retrieves, a third writes, and a fourth verifies. Hugging Face Code Agents make this setup friendly by giving each agent tool use and light coding skills inside safe sandboxes.
Think of it like a pit crew. The planner decides what to do first, the retriever grabs documents, the coder runs small routines to parse or rank, and the editor checks citations. Each member stays in lane yet shares context, which reduces hallucinations and keeps answers tied to evidence the app can show.
A single model tries to plan, search, read, and write all at once. That often looks slick on an easy query, then slips on messy data or multi-step tasks. Splitting work into roles reduces cognitive load for each agent and lets you swap parts without rewiring the whole pipeline.
This structure also helps with failure recovery. If the retrieval looks weak, the planner can ask for another pass with different keywords. If citations look thin, the editor can send the writer back with a clear note. Small loops like this raise quality without burning extra budget on blind retries.
Start with four roles and keep prompts tight. The planner receives the user's request and writes a short plan with named steps and checks. The retriever turns the plan into queries across a vector index and a keyword index, then ranks results. The writer composes a concise answer that cites snippets next to claims. The checker scores groundedness and asks for fixes.
Hugging Face Code Agents attach tools to roles with least privilege. The retriever gets embedding, search, and rerank. The writer gets format helpers. The checker gets a citation validator and a safety scan.
Good retrieval starts with good chunks. Split documents by meaning, not by fixed size alone. Keep headings attached, keep tables intact, and store source ids so you can show links. Use a dual index: semantic vectors for recall and a light keyword filter for precision, then rank with a small cross encoder if latency allows.
Queries work better when the planner rewrites them. It can expand acronyms, add synonyms, and note constraints such as date ranges or file types. After the first pass, let the retriever run an error-aware second pass that learns from empty or noisy results by switching terms or tightening filters.

Prompts should be short, specific, and role-focused. The planner gets rules for breaking a task into named steps. The retriever gets instructions on search types and how many results to return. The writer gets a template that requires quotes or citations next to claims, plus a reminder to say “no source found” when evidence is missing.
Shared memory helps, but it must be tidy. Store a compact scratchpad with the plan, the list of retrieved snippets with ids, and the evolving draft. Avoid dumping entire documents back into context. Link by id and recall only the pieces needed for the current step. It keeps tokens low and focus high.
Code agents shine when a small script turns messy data into clean facts. That might be a table parser, a date normalizer, or a quick calculation. Keep these helpers tiny, deterministic, and well logged. Pass inputs explicitly and capture outputs as structured records that other agents can read.
Safety matters. Run code in a restricted sandbox with timeouts, resource limits, and no network unless you allow a specific fetch tool. Validate file paths, block dangerous imports, and log every tool call with arguments and duration.
Add guardrails that catch common slips. A citation checker can scan sentences for claims and confirm each one traces to a snippet. A groundedness score can compare the draft to sources and raise a flag when the overlap looks thin.
Evaluation needs both offline and live signals. Offline, build a small set of questions, answers, and source triples and score accuracy, citation coverage, and harmful content escapes. Live, track refusal rates, edit distance after human review, and user feedback tags.

Parallelize where it helps and serialize where it keeps order. Retrieval across several indices can run at once, while drafting should wait for ranked snippets. Keep the temperature low for planner and retriever agents, and slightly higher for the writer when style matters. Cache embeddings, query rewrites, and reranking to cut repeated work.
Budget control is simpler with clear roles. You can cap the number of retrieval hops, limit the size of the draft per turn, and clip long plans. If the checker flags thin citations, prefer a targeted retrieval retry over a full pipeline reset. Small, informed retries beat costly guesswork.
Record the plan, tool calls, prompts, snippets, and final answer with hashes and timestamps. Store compact traces so you can replay a run, compare two versions, or roll back a prompt that changed tone. Redact personal data at the edges and keep only what you need for audits and tuning.
Artifacts help teams think together. Save a one-page run report with the user's ask, the plan steps, the retrieved sources, and the checker notes. When a result looks odd, this report turns a long debate into a short fix. It also helps newcomers learn the flow without fishing through raw logs.
Multi-agentic RAG turns a bulky single prompt into a calm workflow where small roles do one job well. With Hugging Face Code Agents, each role uses only the tools it needs, runs tiny helpers safely, and hands tidy outputs to the next role.
Careful chunking, smart query rewrites, focused prompts, and light checks keep answers grounded and traceable. Over time, you get faster replies and responses that arrive with receipts, which is how assistants earn trust over time, consistently.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
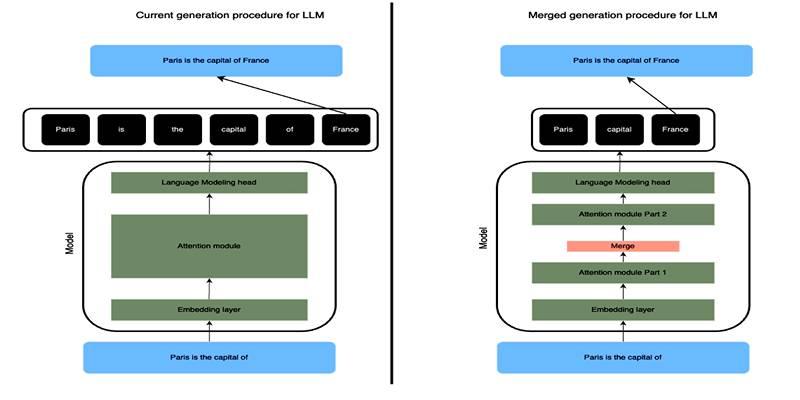
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
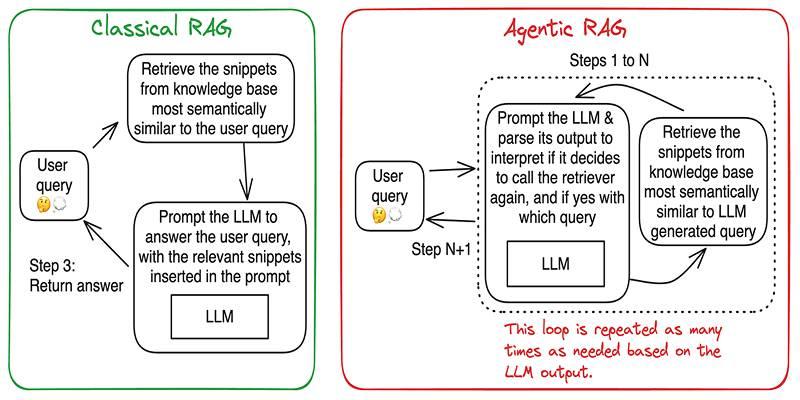
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
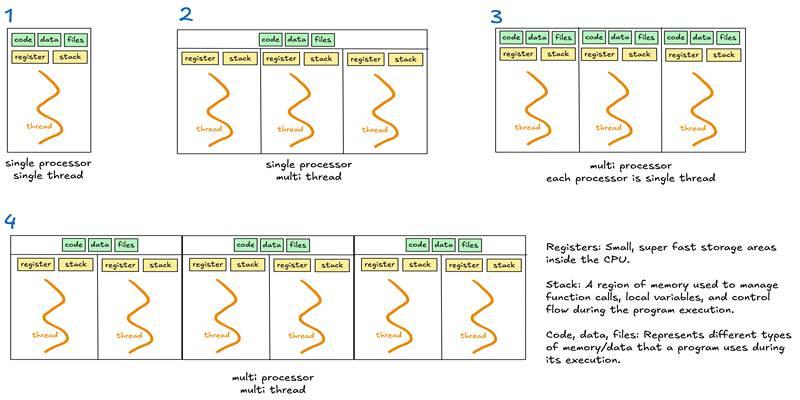
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development