Artificial intelligence is transforming workplaces by automating tasks and delivering powerful data insights. Industries adopting AI see boosts in productivity, accuracy, and employee satisfaction, while those delaying risk falling behind. This guide offers practical strategies to implement AI, from automation tools to advanced analytics, with real-world examples and tips to overcome challenges—helping you stay competitive in a rapidly changing world.

Artificial intelligence refers to diverse technologies capable of carrying out activities that normally demand human intelligence. Algorithms based on machine learning identify trends in data, natural language recognition allows computers to read written text, and automation software allows computers to do work that is monotonous.
The key to successful AI adoption lies in identifying specific problems that technology can solve effectively. Rather than implementing AI for its own sake, focus on areas where intelligent automation can genuinely improve outcomes.
Common workplace applications include document processing, customer service chatbots, predictive analytics for sales forecasting, and automated scheduling systems. Each serves a distinct purpose and addresses particular pain points that many organizations face.
Administrative work often involves repetitive processes that consume valuable time. AI excels at handling these routine tasks, freeing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Intelligent document processing systems can extract information from invoices, contracts, and forms automatically. These tools use optical character recognition combined with machine learning to understand document structure and pull relevant data points.
For example, an accounts payable department might use AI to process hundreds of vendor invoices daily, automatically extracting vendor names, amounts, and due dates while flagging unusual entries for human review.
Smart email filters go beyond basic spam detection. Advanced systems can categorize incoming messages, prioritize urgent communications, and even draft suggested responses for common inquiries.
Customer service teams particularly benefit from AI-powered email management, which can route messages to appropriate specialists based on content analysis and automatically populate response templates with relevant information.
AI scheduling assistants can coordinate meetings across multiple participants, considering time zones, preferences, and availability constraints. These systems learn from past scheduling patterns to suggest optimal meeting times and can even reschedule appointments when conflicts arise.
Customer service represents one of the most successful applications of workplace AI. Intelligent systems can handle routine inquiries while ensuring complex issues reach human agents quickly.
Modern chatbots understand context and can maintain coherent conversations across multiple topics. They handle frequently asked questions, guide customers through troubleshooting processes, and collect initial information before transferring complex cases to human representatives.
The best implementations combine AI efficiency with human empathy, ensuring customers receive appropriate support regardless of their inquiry's complexity.
AI analytics can identify customers likely to experience problems before issues occur. By analyzing usage patterns, support history, and product data, these systems enable proactive outreach that prevents problems rather than simply reacting to complaints.
This approach improves customer satisfaction while reducing overall support volume, creating a more efficient operation that benefits both customers and businesses.
Data-driven decision making becomes more accessible when AI handles the heavy lifting of analysis and pattern recognition.
AI-powered analytics platforms can process vast amounts of business data to identify trends, anomalies, and opportunities that might escape human attention. These systems generate automated reports, create visualizations, and highlight key insights.
Sales teams can use predictive analytics to identify high-value prospects, while operations managers can optimize inventory levels based on demand forecasting algorithms.
Intelligent monitoring systems track key performance indicators across different business functions, automatically alerting managers when metrics deviate from expected ranges. This enables faster response to problems and opportunities.
Marketing teams might use AI to monitor campaign performance across multiple channels, automatically adjusting ad spend based on real-time results and conversion data.
AI doesn't just handle routine tasks—it can also enhance creative and strategic activities by providing inspiration, analysis, and initial drafts that humans can refine.
AI writing assistants help create initial drafts of marketing copy, social media posts, and internal communications. These tools excel at generating multiple variations of content, allowing marketers to test different approaches and messages.
Design AI can create initial concepts for graphics, layouts, and presentations, providing creative starting points that designers can develop further.
AI research assistants can quickly scan large volumes of information to identify relevant studies, trends, and insights. This capability proves particularly valuable for strategic planning, competitive analysis, and market research projects.
Rather than replacing human analysis, these tools accelerate the research phase, allowing professionals to spend more time on interpretation and strategic thinking.
Successfully integrating AI into workplace operations requires careful planning and gradual implementation.
Begin with pilot projects that address specific, well-defined problems. Choose initial applications where success can be measured easily and where failure won't disrupt critical operations. A customer service team might start by implementing a chatbot for basic FAQ responses before expanding to more complex support scenarios.
Employee buy-in is crucial for AI success. Provide comprehensive training that helps team members understand how AI tools complement rather than replace their skills. Emphasize how AI handles routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on more engaging, strategic work that leverages uniquely human capabilities like creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving.
Establish clear metrics for evaluating AI performance and regularly assess results. Track both quantitative measures like processing speed and accuracy, and qualitative factors such as employee satisfaction and customer feedback. Use performance data to refine AI systems continuously, adjusting parameters and expanding capabilities based on real-world usage patterns.
Organizations often encounter predictable obstacles when introducing AI solutions. Understanding these challenges helps develop effective mitigation strategies.
AI systems require high-quality data to function effectively. Many organizations discover that their data is fragmented, inconsistent, or incomplete when they begin AI implementation. Address data issues before deploying AI solutions by establishing data governance practices, cleaning existing datasets, and implementing consistent data collection procedures.
Employee concerns about job displacement or increased monitoring are natural responses to AI introduction. Address these concerns through transparent communication about AI's role and benefits. Involve employees in the selection and implementation process, seeking their input on which tasks would benefit most from automation and how AI tools should be configured.
Unlock AI’s potential at work by identifying tasks where automation saves time and resources. Start with small pilot projects to show clear benefits before scaling up. Prioritize training and change management to ensure smooth adoption and maximize ROI. The future belongs to companies that combine AI with human creativity. A strategic approach can transform your workplace into a more efficient, productive, and engaging environment.

How AI with multiple personalities enables systems to adapt behaviors across user roles and tasks

Effective AI governance ensures fairness and safety by defining clear thresholds, tracking performance, and fostering continuous improvement.

Explore the truth behind AI hallucination and how artificial intelligence generates believable but false information
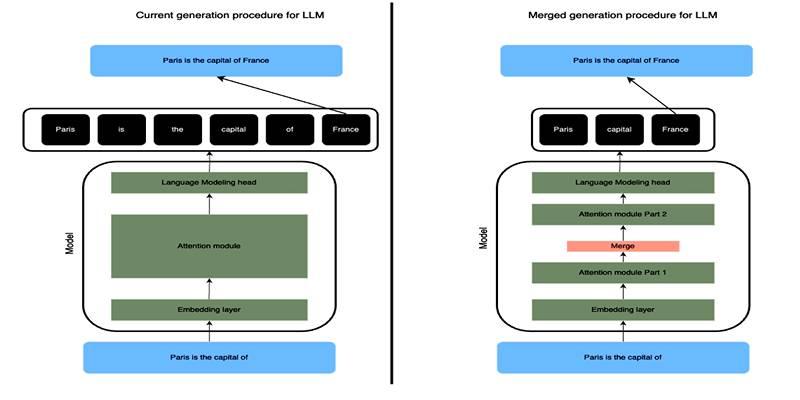
Learn how SLERP token merging trims long prompts, speeds LLM inference, and keeps output meaning stable and clean.

How to approach AI trends strategically, overcome FOMO, and turn artificial intelligence into a tool for growth and success.
Explore how Keras 3 simplifies AI/ML development with seamless integration across TensorFlow, JAX, and PyTorch for flexible, scalable modeling.

Craft advanced machine learning models with the Functional API and unlock the potential of flexible, graph-like structures.

How to avoid common pitfalls in data strategy and leverage actionable insights to drive real business transformation.

How neural networks revolutionize time-series data imputation, tackling challenges in missing data with advanced, adaptable strategies.
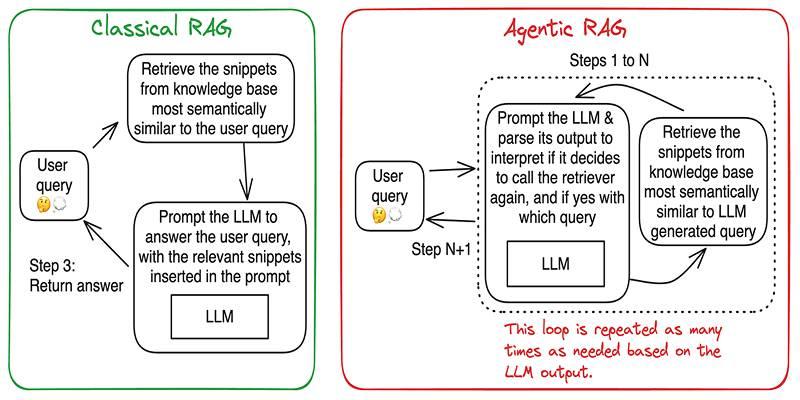
Build accurate, explainable answers by coordinating planner, retriever, writer, and checker agents with tight tool control.
Learn when to use threads, processes, or asyncio to handle I/O waits, CPU tasks, and concurrency in real-world code.

Discover DeepSeek’s R1 training process in simple steps. Learn its methods, applications, and benefits in AI development